Scrum is a framework for project management, normally present on Agile Software Development.
Scrum is based in an article “The New Product Development Game”. In the article, authors suggest a new approach to product development using the rugby approach.
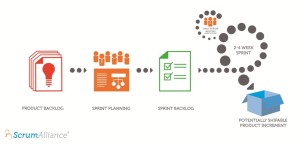
This framework is based on constant periods of time, called Sprints, to develop the features. Usually take 2 to 4 weeks.
The structure of the Scrum framework is composed of three roles, six meetings and four artifacts: The team is divided into three roles:
- Product Owner: Person responsible for maximizing the value of work;
- Scrum Master: Person responsible for ensuring that the team works and is productive;
- Team: Members of the team that are self-sufficient to do their job.
There are six types of meetings:
- Sprint planning: The team meets with the product owner to select the tasks for the sprint;
- Daily meeting: The team meet every day, usually lasting 15 minutes, in order to update the Burndown chart and every team member responds to three different questions: “What have you done since yesterday?”, “What are you planning to do today?” and “Any impediments/stumbling blocks?”.
- Sprint reviews: The team demonstrates the functionality to the product owner made during the sprint.
- Sprint retrospectives: The team searches for new ways to improve the process and product.
In SCRUM, four types of artifacts are produced
- Product Backlog: An ordered list of prioritized project features, from highest to lowest. It is dynamic and can be modified at any time as needed during the project lifetime
- Sprint Backlog: A set of features taken from the product backlog (from highest to lowest priority) that team is committed to execute in the sprint. These features are divided into small tasks that are assigned to the team members.
- Burndown charts of the sprint and delivery: It is a graphical representation that allows the verification of the tasks status.